- Home
- Scans for Women
- Scans for Men
- Msk
- Pregnancy
- Cardiovascular
- About
- Book a Scan
- Blog
Accurate measurements and weight estimation to ensure your baby is growing healthily
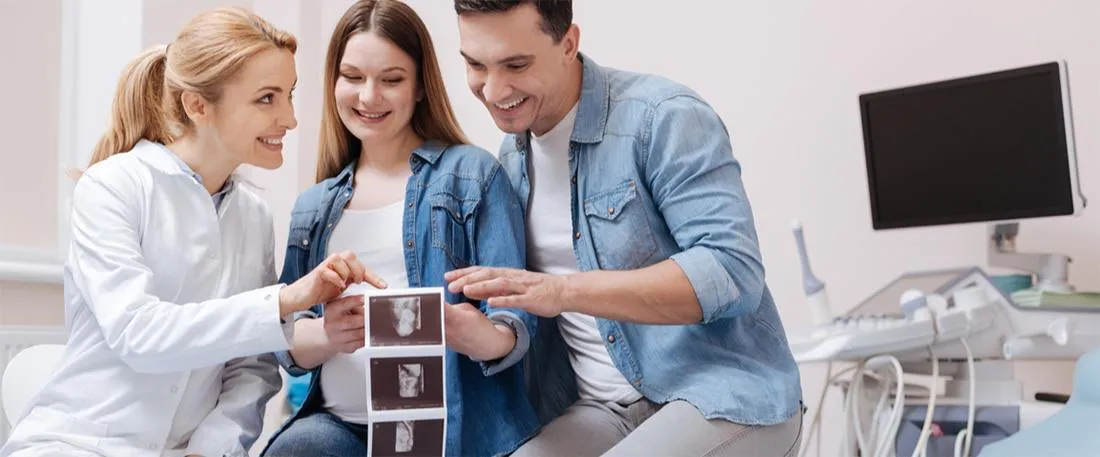

A growth scan provides precise measurements of your baby's size and development in the third trimester. Using standardised growth charts, we can tell you which percentile your baby is tracking and whether growth is progressing normally.
We measure three key parameters—head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femur length—to calculate your baby's estimated weight. This helps identify babies who are smaller or larger than expected for their gestational age, allowing for appropriate monitoring and planning.
Whether you have risk factors like gestational diabetes or high BMI, your midwife has concerns about fundal height, or you simply want reassurance that your baby is thriving, our growth scans provide expert assessment in a caring environment.
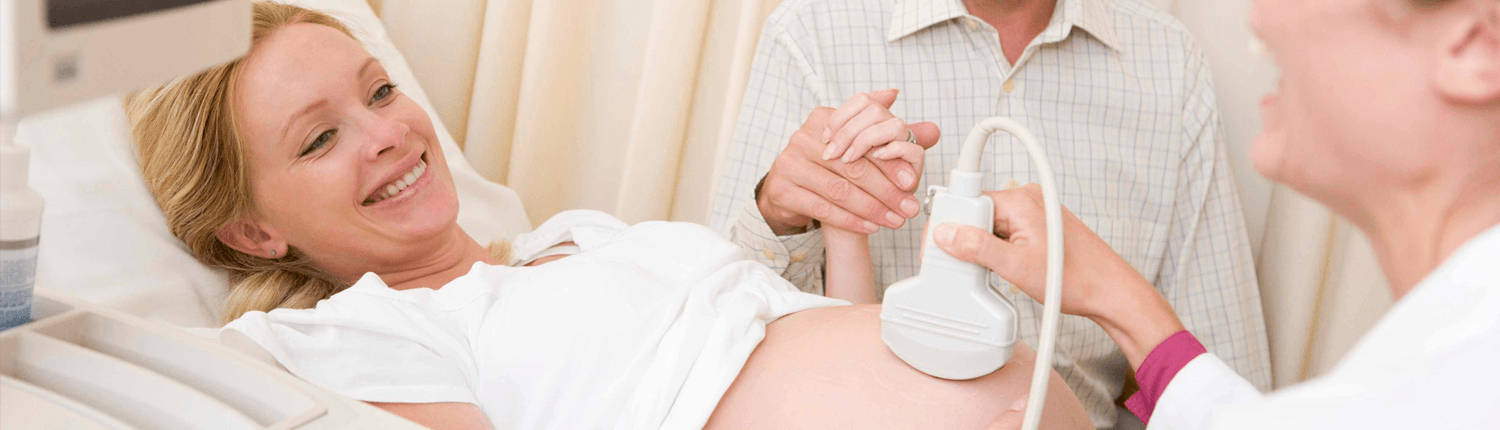
Comprehensive measurements and assessment to monitor your baby's development
We measure around your baby's head at the widest point to assess brain growth and overall development.
Measurement around your baby's abdomen provides important information about nutrition and liver growth. The AC is the most sensitive indicator of growth issues.
We measure your baby's thigh bone (femur) to assess skeletal growth and calculate overall length.
Using the HC, AC, and FL measurements, we calculate your baby's estimated weight with specialised formulas validated for accuracy.
We plot your baby's measurements on customised growth charts to determine which percentile your baby is tracking (e.g., 50th, 75th percentile).
We assess the amount of fluid surrounding your baby, as low or high fluid levels can indicate growth or placental issues.
We check your placenta's position, appearance, and grade to ensure it's functioning properly to support your baby's growth.
If growth restriction is suspected, we use Doppler ultrasound to assess blood flow through the umbilical cord and placenta.
You'll receive a comprehensive written report with all measurements, percentiles, and recommendations to share with your midwife or obstetrician.
This scan is especially valuable if you have risk factors or concerns about your baby's size
If you have gestational diabetes, regular growth scans help monitor for macrosomia (large baby) and guide delivery planning.
If your midwife has concerns that your bump is measuring small or large for your dates based on fundal height measurements.
If you've previously had a baby with growth restriction (IUGR) or macrosomia, growth monitoring helps ensure optimal outcomes this time.
Maternal BMI outside the normal range can affect fetal growth patterns and may warrant closer monitoring.
If you've noticed your baby moving less than usual, a growth and wellbeing scan can provide reassurance or identify issues.
Many parents simply want reassurance in the third trimester that their baby is growing well and thriving.
Choose a convenient appointment time online or call us on 020 3633 4902. Same-day and next-day appointments are often available.
We're at 29 Weymouth Street, easily accessible from Oxford Circus and Regent's Park tube. Your partner is very welcome to join you.
Our experienced sonographer will welcome you, explain the scan process, and answer any questions you have.
We'll perform a detailed abdominal ultrasound, taking precise measurements of your baby's head, abdomen, and femur, and assessing fluid and placenta.
Your sonographer will calculate your baby's estimated weight, explain which percentile your baby is on, and discuss what the findings mean.
You'll receive printed photos and a comprehensive growth report with all measurements and recommendations to share with your healthcare team.

All-inclusive Growth Scan
"I have gestational diabetes so was worried about my baby's size. Had a growth scan at 32 weeks and another at 36 weeks. The measurements were so reassuring and the sonographer explained everything clearly. Baby was tracking perfectly on the 60th percentile. Highly recommend for anyone with GD."
"My midwife said my bump was measuring small so referred me for a growth scan. The sonographer was wonderful—she took her time with all the measurements and showed me baby was actually growing beautifully on the 45th percentile. Such a relief. The detailed report put everyone's mind at ease."
"Had my first baby at 8lbs 12oz so wanted to monitor this one's growth. Growth scans at 28, 32, and 36 weeks showed baby tracking on the 85th percentile but not too big. Really helpful for planning my delivery. Professional service and same-day appointments available."
Book your Growth Scan today and get expert assessment of your baby's development
📍 Sonoworld London
29 Weymouth Street, Marylebone, London W1G 7DB
Get directions